BIOSOLETRANDO ORGANELAS Prof. Valdiran Wanderley de Souza.
Transcript of BIOSOLETRANDO ORGANELAS Prof. Valdiran Wanderley de Souza.

BIOSOLETRANDO
ORGANELAS
Prof. Valdiran Wanderley de Souza


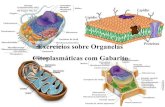
E U C A R I O N T E A N I M A L
CARACTERÍSTICAS
• Possui núcleo.


L I S O S S O M O S
FUNÇÃO
• Responsáveis pela digestão celular.
Enzima Hidrólase ácida


M I C R O F I L A M E N T O S
FUNÇÃO
• Formam o citoesqueleto.


R I B O S S O M O S
FUNÇÃO
• Síntese de proteínas por meio da união de aminoácidos.


E U C A R I O N T E V E G E T A L
CARACTERÍSTICAS
• Possui núcleo.• Parede celulósica.• Organela especial:
cloroplasto.


C O M P L E X O G O L G I E N S E
FUNÇÃO
• Empacotar e secretar proteínas.
• Síntese de lipídios.• Em células vegetais
produz nova parede celular durante a divisão celular.
• Formam o acrossoma dos espermatozóides.


R E T Í C U L O E N D O P L A S M Á T I C O N Ã O-G R A N U L O S O
FUNÇÃO
• Síntese de lipídios.• Síntese de enzimas
responsáveis pela desintoxicação do organismo.
• Reservatório de íons de cálcio.
• Transporte de várias substâncias.


C E N T R Í O L O S
FUNÇÃO
• Organizam os fusos acromáticos durante a divisão celular.
• Formam os cílios e os flagelos.


P E R O X I S S O M A S
FUNÇÃO
• Decompõem a água oxigenada em água e oxigênio.


C L O R O P L A S T O S
FUNÇÃO
• Responsável pela absorção da luz solar para transformação do gás carbônico e água em açúcares.


F L A G E L O S
FUNÇÃO
• Servem para locomoção ou para facilitar a captura de alimentos.
?
?


CÉLULA P R O C A R I O N T E
CARACTERÍSTICAS
• Não possui núcleo.• Organela presente:
ribossomo.


V A C Ú O L O DO SULCO CELULAR
FUNÇÃO
• Responsáveis pela regulação do equilíbrio osmótico.
• Em células vegetais servem para armazenamento de substâncias.
???


P O L I S S O M A
DEFINIÇÃO
• Agrupamento de Ribossomos no citoplasma.


C Í L I O S
FUNÇÃO
• Servem para locomoção ou para facilitar a captura de alimentos.


C I C L O S E
DEFINIÇÃO
• Espécie de corrente citoplasmática, característica de células vegetais, também depende das contrações da actina.


COMPLEXO GOLGIENSE
FUNÇÃO
• Síntese de proteínas e o transporte de várias substâncias.


C I T O E S Q U E L E T O
FUNÇÃO
• Ajudar a manter a forma da célula.
• Serve de sustentação às estruturas celulares.
• Participa de diversos movimentos celulares.


C L O R O P L A S T O S
FUNÇÃO
• Responsável pela absorção da luz solar para transformação do gás carbônico e água em açúcares.


C E N T R Í O L O S
FUNÇÃO
• Organizam os fusos acromáticos durante a divisão celular.
• Formam os cílios e os flagelos.


M I C R O T Ú B U L O S
FUNÇÃO
• Formam o citoesqueleto, cílios e flagelos.


M I T O C Ô N D R I A S
FUNÇÃO
• Responsável pelas etapas finais da respiração celular aeróbia nos eucariontes e pelos processos anaeróbios de obtenção de energia.


R E T Í C U L O E N D O P L A S M Á- T I C O N Ã O-G R A N U L O S O
FUNÇÃO
• Empacotar e secretar proteínas.
• Síntese de lipídios.• Em células vegetais
produz nova parede celular durante a divisão celular.
• Formam o acrossoma dos espermatozóides.


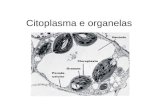
C I T O S O L
FUNÇÃO
• Local onde realizam-se diversas reações químicas do metabolismo.
????????


E U C A R I O N T E A N I M A L
CARACTERÍSTICAS
• Possui núcleo.• Organela especial:
centríolos.


C E N T R Í O L O S
FUNÇÃO
• Organizam os fusos acromáticos durante a divisão celular.
• Formam os cílios e os flagelos.


E U C A R I O N T E A N I M A L
CARACTERÍSTICAS
• Possui núcleo.• Organela especial:
centríolos.


M O V I M E N T O A M E B Ó I D E
DEFINIÇÃO
• Dependente da contração da actinia e de pseudópodes serve para locomoção e captura de alimentos pelas amebas.


P R O C A R I O N T E
CARACTERÍSTICAS
• Não possui núcleo.• Organela presente:
ribossomo.


M I T O C Ô N D R I A S
FUNÇÃO
• Responsável pelas etapas finais da respiração celular aeróbia nos eucariontes e pelos processos anaeróbios de obtenção de energia.


C Í L I O S
FUNÇÃO
• Servem para locomoção ou para facilitar a captura de alimentos.


E U C A R I O N T E V E G E T A L
CARACTERÍSTICAS
• Possui núcleo.• Parede celulósica.• Organela especial:
cloroplasto.


F L A G E L O S
FUNÇÃO
• Servem para locomoção ou para facilitar a captura de alimentos.


C L O R O P L A S T O S
FUNÇÃO
• Responsável pela absorção da luz solar para transformação do gás carbônico e água em açúcares.


R E T Í C U L O E N D O P L A S- M Á T I C O G R A N U L O S O
FUNÇÃO
• Síntese de proteínas e o transporte de várias substâncias.


E U C A R I O N T E A N I M A L
CARACTERÍSTICAS
• Possui núcleo.• Organela especial:
centríolos.


C I T O E S Q U E L E T O
FUNÇÃO
• Ajudar a manter a forma da célula.
• Serve de sustentação às estruturas celulares.
• Participa de diversos movimentos celulares.


C E N T R Í O L O S
FUNÇÃO
• Organizam os fusos acromáticos durante a divisão celular.
• Formam os cílios e os flagelos.


R E T Í C U L O E N D O P L A S- M Á T I C O G R A N U L O S O
FUNÇÃO
• Síntese de proteínas e o transporte de várias substâncias.


F L A G E L O S
FUNÇÃO
• Servem para locomoção ou para facilitar a captura de alimentos.


V A C Ú O L O CONTRÁCTIL
FUNÇÃO
• Responsáveis pela regulação do equilíbrio osmótico.


M I T O C Ô N D R I A S
FUNÇÃO
• Responsável pelas etapas finais da respiração celular aeróbia nos eucariontes e pelos processos anaeróbios de obtenção de energia.


R E T Í C U L O E N D O P L A S M Á T I C O N Ã O-G R A N U L O S O
FUNÇÃO
• Empacotar e secretar proteínas.
• Síntese de lipídios.• Em células vegetais
produz nova parede celular durante a divisão celular.
• Formam o acrossoma dos espermatozóides.


FUNÇÃO
• Processo de digestão intracelular..
VACUOLO DIGESTIVO


C I T O E S Q U E L E T O
FUNÇÃO
• Ajudar a manter a forma da célula.
• Serve de sustentação às estruturas celulares.
• Participa de diversos movimentos celulares.